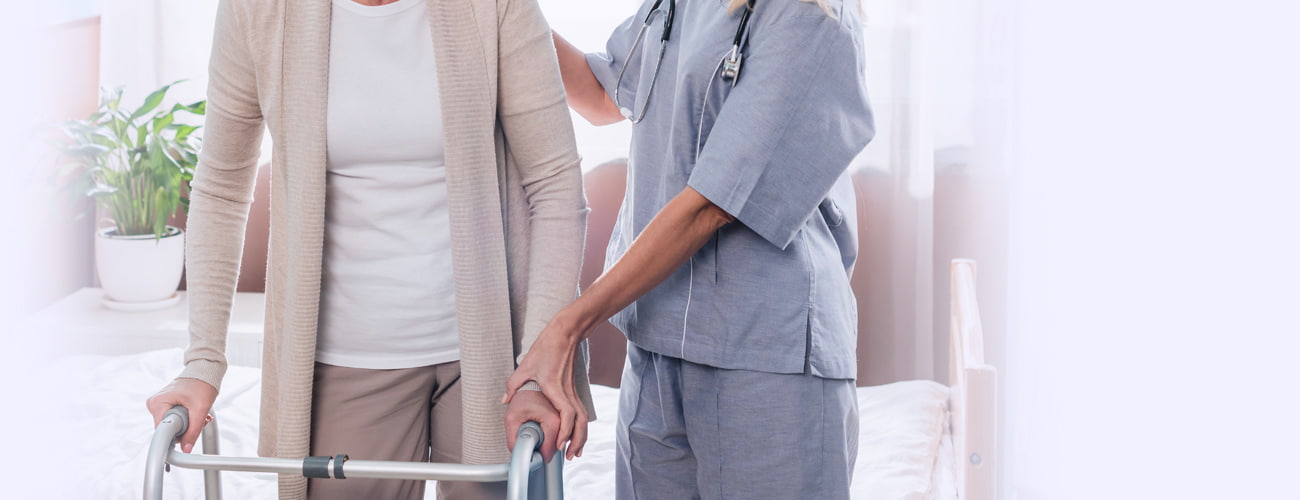
Families trust nursing homes and assisted living facilities to keep their loved ones safe, clean, and properly cared for. When a facility in Prince George’s County fails to meet that basic obligation — through understaffing, inadequate training, or outright indifference — residents suffer preventable injuries that can be life-threatening. Maryland law provides legal remedies for nursing home neglect, including the right to file a civil lawsuit for damages and to report the facility to state regulators. Lebowitz & Mzhen Personal Injury Lawyers holds negligent nursing homes accountable across Prince George’s County and throughout Maryland, with over $90 million recovered for injured clients and their families.
What Is Nursing Home Neglect Under Maryland Law?
Nursing home neglect occurs when a facility fails to provide a resident with the care and services necessary to maintain their health, safety, and well-being. Unlike abuse, which involves intentional harm, neglect results from the facility’s failure to act. Under Md. Code, Health-Gen. § 19-347, Maryland nursing home residents have the right to adequate and appropriate medical care, freedom from neglect, and a safe living environment.
 Maryland Nursing Home Lawyer Blog
Maryland Nursing Home Lawyer Blog